Version Control Integration in PyCharm: Mastering Git Workflows Without Leaving Your IDE
Modern software development is unthinkable without version control, and Git has become the de facto standard for managing code changes. While many developers are comfortable with Git command-line operations, PyCharm's built-in Git integration offers a powerful alternative that can significantly streamline your workflow and boost productivity.
Why Use PyCharm's Git Integration?
PyCharm provides a comprehensive visual interface for Git operations that eliminates the need to memorize complex command-line syntax. The integration is seamless, context-aware, and designed to help you focus on writing code rather than managing version control mechanics. Whether you're a Git novice or an experienced developer, PyCharm's tools can enhance your efficiency.
The IDE automatically detects Git repositories in your projects and provides instant access to version control features through intuitive menus, keyboard shortcuts, and visual indicators. This tight integration means you can perform most Git operations without ever leaving your coding environment.
Setting Up Git in PyCharm
Before diving into Git workflows, ensure PyCharm is properly configured to work with Git. Navigate to File > Settings > Version Control > Git (or PyCharm > Preferences on macOS) and verify that PyCharm has detected your Git installation.
C:\Program Files\Git\bin\git.exe, while on Unix-based systems, it's usually /usr/bin/git.
Committing Changes: The Visual Approach
One of PyCharm's most powerful features is its commit interface, which provides a comprehensive view of all changes before you commit them. Access the commit tool window by pressing Ctrl+K (or Cmd+K on macOS) or selecting VCS > Commit from the menu.
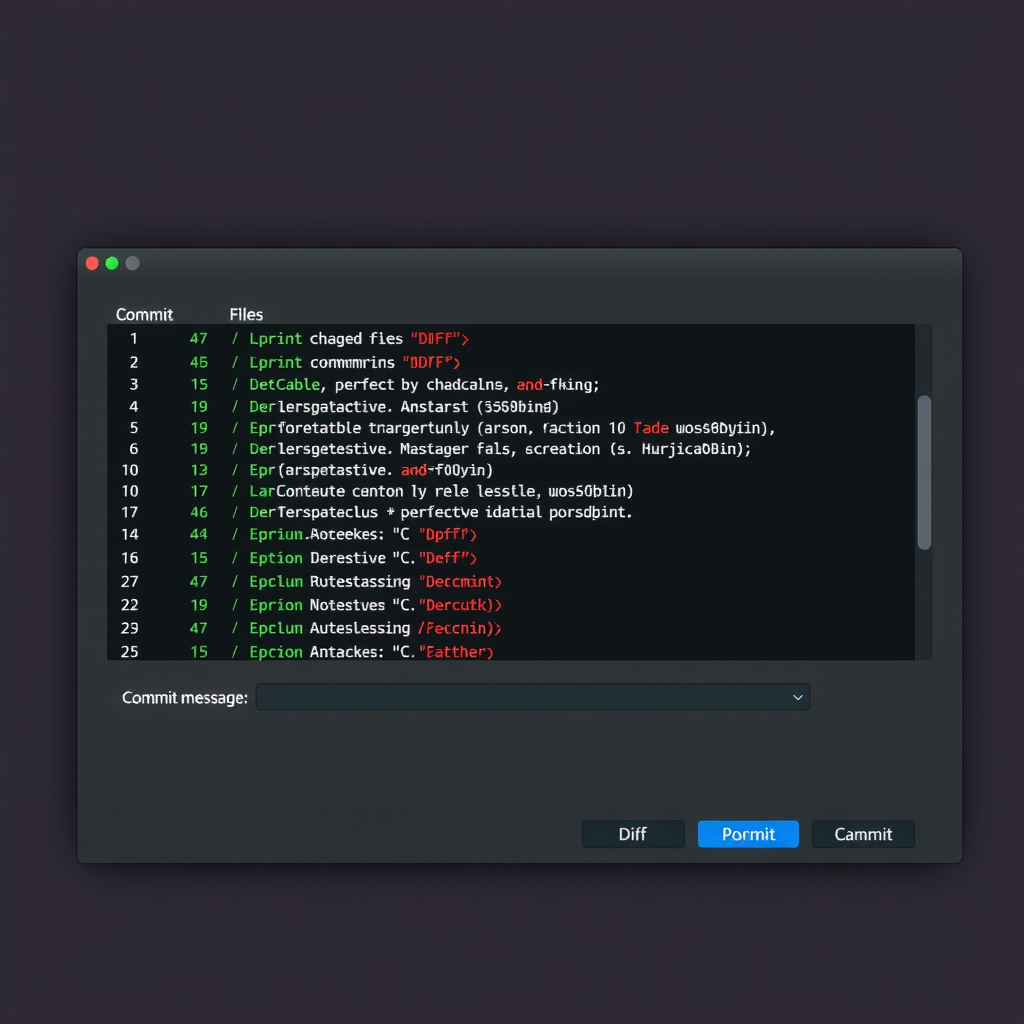
The commit window displays all modified files in a tree structure, allowing you to review changes file by file. PyCharm's diff viewer highlights additions in green and deletions in red, making it easy to understand exactly what has changed. You can even stage specific chunks of code rather than entire files, giving you granular control over your commits.
Key Features of PyCharm's Commit Interface
- Intelligent Code Analysis: PyCharm automatically runs code inspections before committing, alerting you to potential issues like syntax errors, unused imports, or code style violations.
- Commit Message Templates: Configure templates for commit messages to maintain consistency across your team and ensure all necessary information is included.
- Partial Commits: Select specific changes within a file to commit, allowing you to create more focused, logical commits even when you've made multiple unrelated changes.
- Amend Commits: Easily amend the last commit if you forgot to include a file or need to update the commit message.
Branch Management Made Simple
Managing branches in PyCharm is remarkably straightforward. The Git Branches popup, accessible via VCS > Git > Branches or by clicking the branch name in the status bar, provides quick access to all branch operations.
From this popup, you can create new branches, switch between existing branches, merge branches, and even perform more advanced operations like rebasing. PyCharm intelligently handles the underlying Git commands, ensuring that your working directory is properly updated and any conflicts are clearly identified.
Create new branch: VCS > Git > Branches > New Branch
Switch to branch: Click branch name in status bar
Merge branch: VCS > Git > Merge Changes
Delete branch: Right-click branch > Delete
Checkout remote branch: VCS > Git > Branches > Remote BranchesWorking with Feature Branches
PyCharm excels at supporting feature branch workflows. When you create a new branch for a feature, PyCharm tracks all changes made on that branch and provides clear visual indicators in the editor gutter showing which lines have been modified. This makes it easy to understand the scope of your changes at a glance.
The IDE also supports branch comparison, allowing you to see all differences between your current branch and any other branch. This is particularly useful before merging to ensure you understand exactly what changes will be integrated.
Resolving Merge Conflicts with Confidence
Merge conflicts are an inevitable part of collaborative development, but PyCharm's conflict resolution tools make them far less intimidating. When a merge conflict occurs, PyCharm presents a three-way merge viewer that displays your changes, the incoming changes, and the common ancestor side by side.
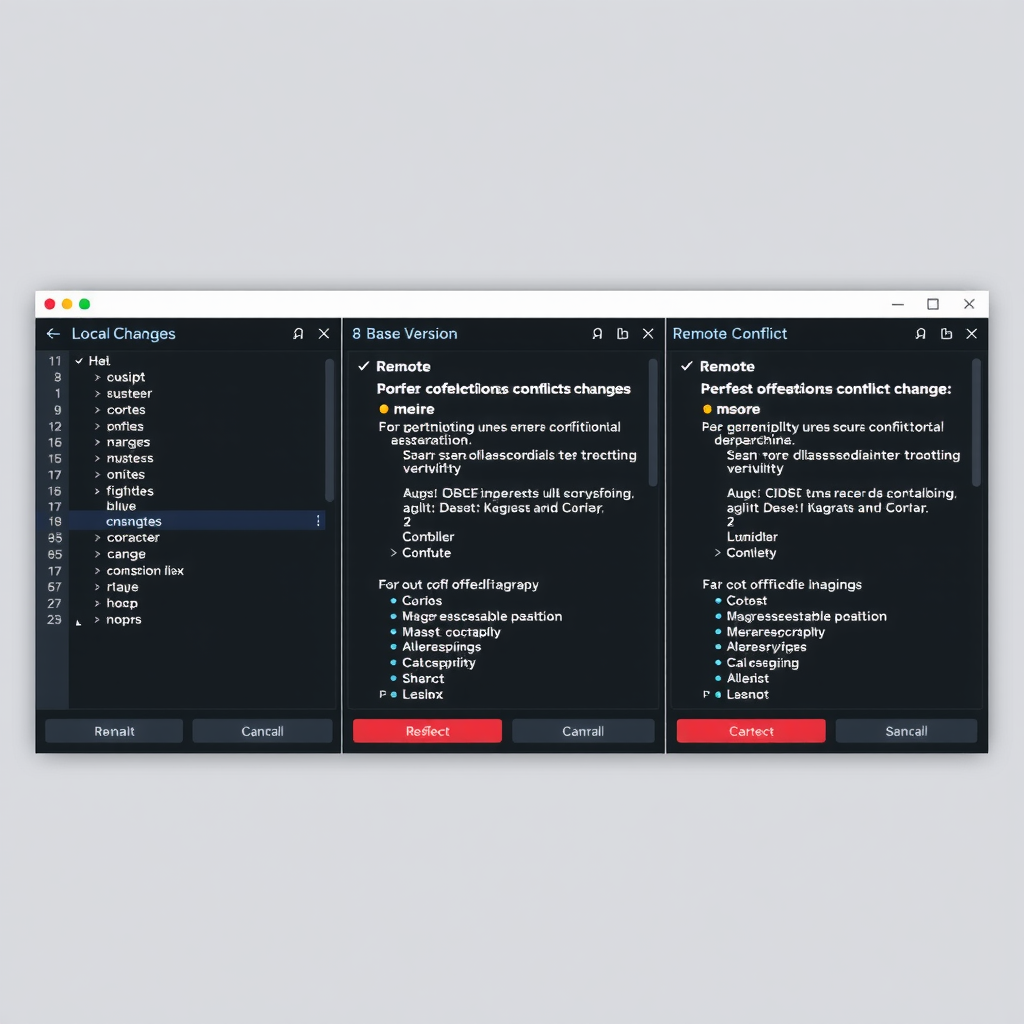
The merge tool allows you to accept changes from either side with a single click, or manually edit the result to create a custom resolution. PyCharm highlights conflicting sections in red and provides intuitive buttons to accept left, accept right, or merge both changes.
Advanced Conflict Resolution Features
- Smart Merge: PyCharm can automatically resolve simple conflicts where changes don't overlap, saving you time on straightforward merges.
- Syntax Highlighting: The merge viewer maintains full syntax highlighting, making it easier to understand the code context during conflict resolution.
- Navigation Tools: Quickly jump between conflicts using keyboard shortcuts, allowing you to efficiently resolve multiple conflicts in large files.
- Undo/Redo: Full undo/redo support during conflict resolution means you can experiment with different resolutions without fear of making mistakes.
Collaborating with Remote Repositories
PyCharm seamlessly integrates with remote Git repositories, whether hosted on GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, or any other Git hosting service. The IDE provides dedicated tools for pushing, pulling, and fetching changes, all accessible through the VCS menu or keyboard shortcuts.
When you push changes, PyCharm shows you exactly what commits will be pushed and to which branch. If there are conflicts with the remote repository, PyCharm alerts you immediately and guides you through the resolution process. The IDE also supports pull requests and code reviews directly from the interface when connected to supported hosting services.
GitHub Integration
PyCharm offers particularly strong integration with GitHub. You can clone repositories, create pull requests, review code, and manage issues without leaving the IDE. The GitHub integration includes:
- Direct authentication with your GitHub account
- Pull request creation and management from the IDE
- Code review tools with inline commenting
- Issue tracking and linking commits to issues
- Gist creation and management
Viewing History and Annotations
Understanding the history of your codebase is crucial for effective development. PyCharm provides multiple ways to explore Git history, from the comprehensive Git Log tool window to inline annotations that show who last modified each line of code.
The Git Log window (Alt+9) displays a visual representation of your repository's commit history, including branch structure and merge points. You can filter commits by author, date, branch, or search for specific changes. Clicking on any commit shows the full diff of changes made in that commit.
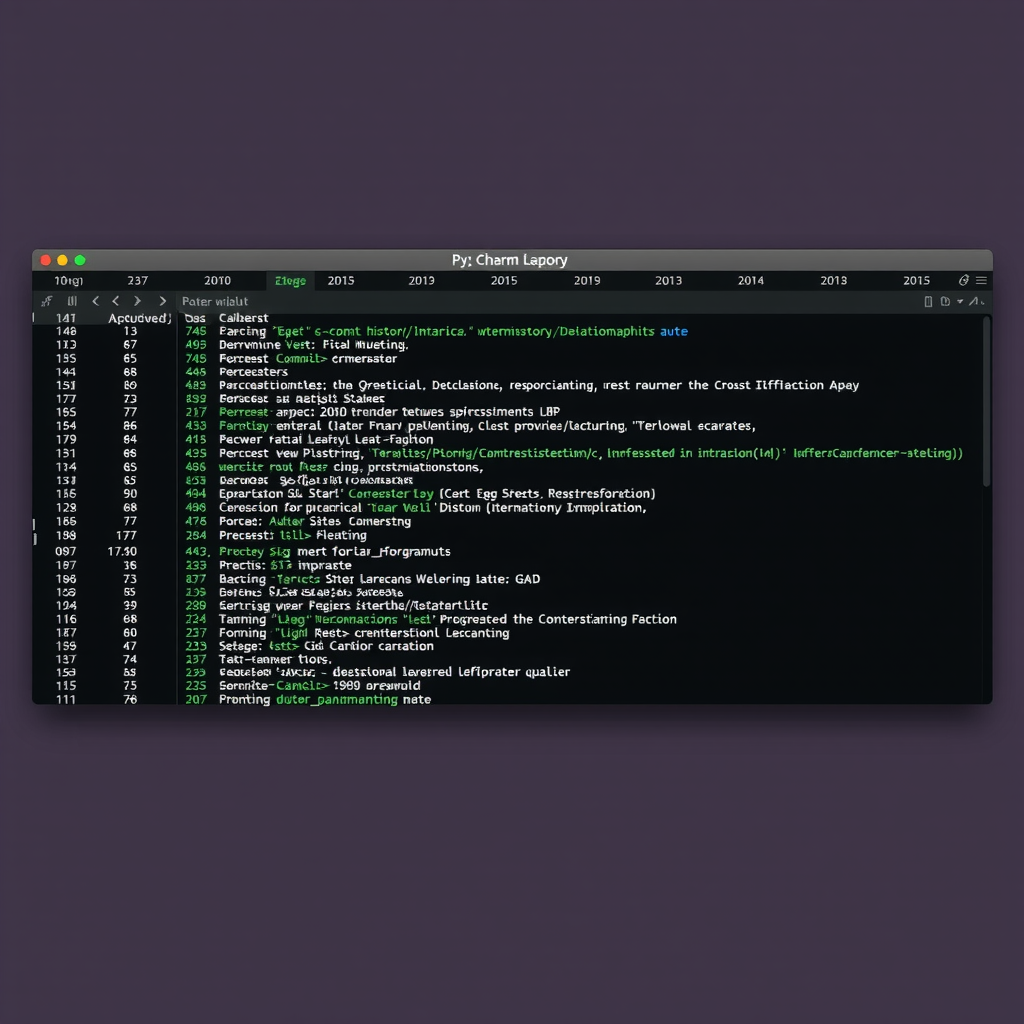
Git Blame and Annotations
The Annotate feature (right-click in the editor gutter and select Annotate with Git Blame) shows who last modified each line of code and when. This is invaluable for understanding the context of changes and identifying the right person to ask about specific code sections.
PyCharm's annotations are interactive—clicking on an annotation opens the full commit that introduced that change, allowing you to see the complete context of the modification. You can also navigate through the history of a specific line, seeing all previous versions and who changed them.
Advanced Git Operations
Beyond basic Git operations, PyCharm supports advanced workflows that can significantly enhance your productivity. These include interactive rebasing, cherry-picking commits, stashing changes, and working with Git submodules.
Interactive Rebase
PyCharm's interactive rebase tool allows you to rewrite commit history in a visual, intuitive way. You can reorder commits, squash multiple commits into one, edit commit messages, or drop commits entirely. The IDE presents a clear interface showing all commits in the rebase and allows you to drag and drop to reorder them.
Stashing Changes
The stash feature allows you to temporarily save uncommitted changes and return to a clean working directory. This is useful when you need to switch branches quickly but aren't ready to commit your current work. PyCharm's stash interface (VCS > Git > Uncommitted Changes > Stash Changes) lets you create named stashes, view all stashed changes, and apply or drop stashes as needed.
Productivity Tips and Keyboard Shortcuts
Mastering PyCharm's Git integration means learning the keyboard shortcuts that can dramatically speed up your workflow. Here are some essential shortcuts to memorize:
Best Practices for Git in PyCharm
To get the most out of PyCharm's Git integration, follow these best practices:
- Commit Often, Commit Small: Make frequent, focused commits that address single concerns. PyCharm's partial commit feature makes this easy even when you've made multiple changes.
- Write Meaningful Commit Messages: Use PyCharm's commit message templates and take advantage of the spell checker to write clear, descriptive commit messages.
- Review Before Committing: Always review the diff before committing. PyCharm's visual diff viewer makes it easy to catch unintended changes.
- Use Feature Branches: Create a new branch for each feature or bug fix. PyCharm makes branch creation and switching effortless.
- Keep Your Local Repository Updated: Regularly pull changes from the remote repository to minimize merge conflicts.
- Leverage Code Inspections: Enable pre-commit code analysis to catch issues before they enter the repository.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with PyCharm's excellent Git integration, you may occasionally encounter issues. Here are solutions to common problems:
PyCharm Not Detecting Git Repository
If PyCharm doesn't recognize your Git repository, ensure that the .git directory exists in your project root. You can manually enable Git for a project by going to VCS > Enable Version Control Integration and selecting Git.
Authentication Issues with Remote Repositories
If you're having trouble pushing or pulling from remote repositories, check your authentication settings in Settings > Version Control > GitHub/GitLab. For HTTPS repositories, you may need to use a personal access token instead of a password. For SSH repositories, ensure your SSH keys are properly configured.
Merge Conflicts That Won't Resolve
If you're stuck in a merge conflict state, you can abort the merge by going to VCS > Git > Abort Merge. This will return your repository to the state before the merge attempt. You can then try the merge again or seek help from team members.
Conclusion
PyCharm's Git integration transforms version control from a necessary chore into a seamless part of your development workflow. By mastering the tools and techniques covered in this guide, you can commit changes more confidently, manage branches more effectively, resolve conflicts more efficiently, and collaborate with your team more productively—all without leaving your IDE.
The visual, intuitive interface removes much of the complexity traditionally associated with Git, making version control accessible to developers of all skill levels. Whether you're working on a solo project or collaborating with a large team, PyCharm's Git integration provides the tools you need to maintain a clean, organized codebase.
Take the time to explore PyCharm's Git features, experiment with different workflows, and customize the settings to match your preferences. With practice, you'll find that version control becomes second nature, allowing you to focus on what really matters: writing great code.